A graph-based approach to closed-domain natural language generation
Graph-based Natural Language Processing (NLP) methods have seen significant advancements in recent years with the development of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG). LLMs are sophisticated models that recognize numerous NLP tasks by analyzing the users' natural language instructions called prompts. However, their industrial use is questionable due to such ethical concerns as false information generation called hallucinations, high risks of data breaches, and plagiarism. The paper introduces a novel NLP architecture, the Graph-Based Block-to-Block Generation (G3BG), which leverages state-of-the-art deep learning techniques, the power of attention mechanisms, distributional semantics, graph-based information retrieval, and decentralized networks. The model encodes user prompts to mitigate data breach risk, retrieves relevant information from a graph knowledge base, and forms a block for a conditional language model using LLMs to perform a new secure type of RAG. The model is closed-domain and small-scale oriented. It exhibits superior performance across low-resource NLP tasks, which makes it prominent for industrial use. The research presents a novel graph-based dataset. The dataset comprises private data features to encode and closed-domain textual information for information retrieval. The dataset is used to train and evaluate the G3BG model. The model allows cutting 100x training dataset volume achieving Perplexity ~6.51 on the Language Generation task and F1-Score ~90.3 on the Information Retrieval task comparable to most state-of-the-art language models. The experimental results prove the effectiveness of the proposed method and contribute to the algorithmic approaches toward LLM risk mitigation.
Figures
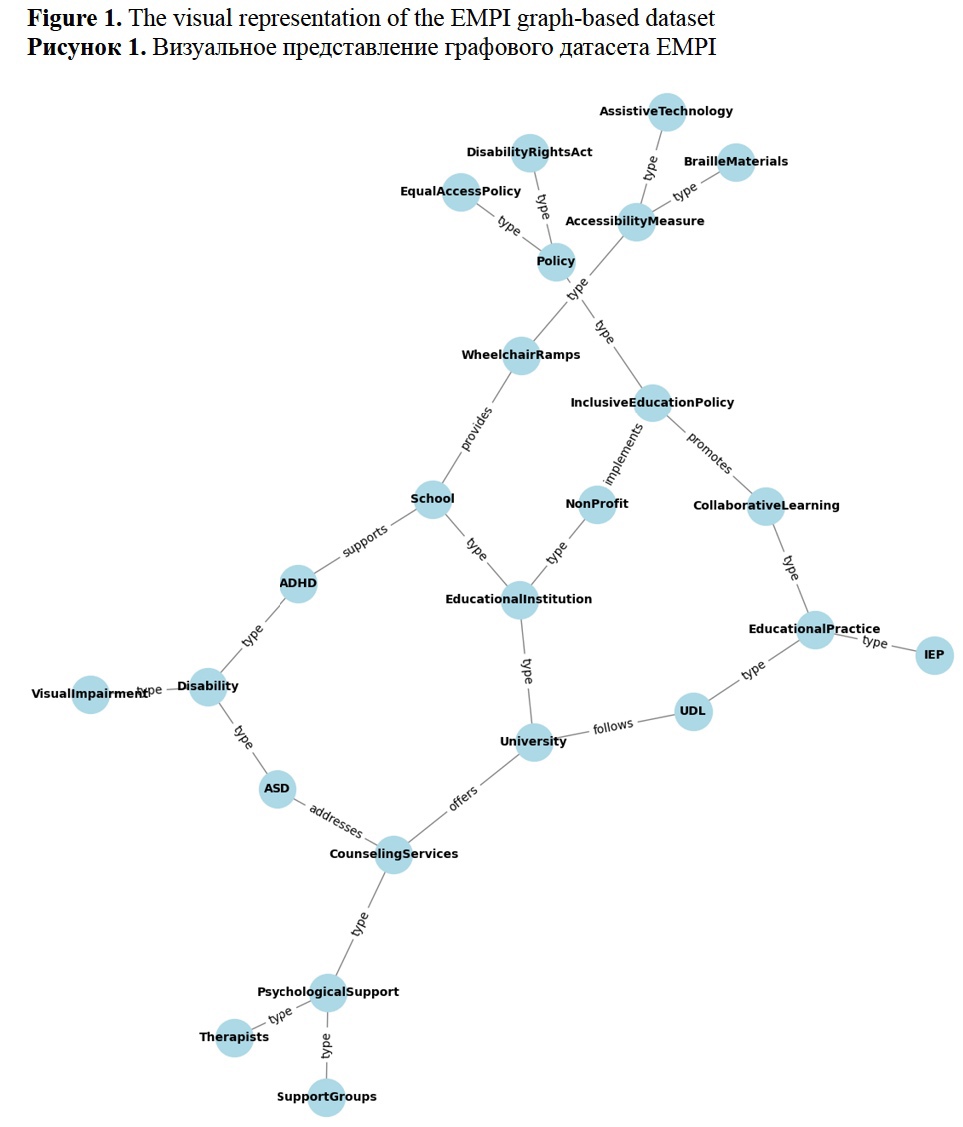
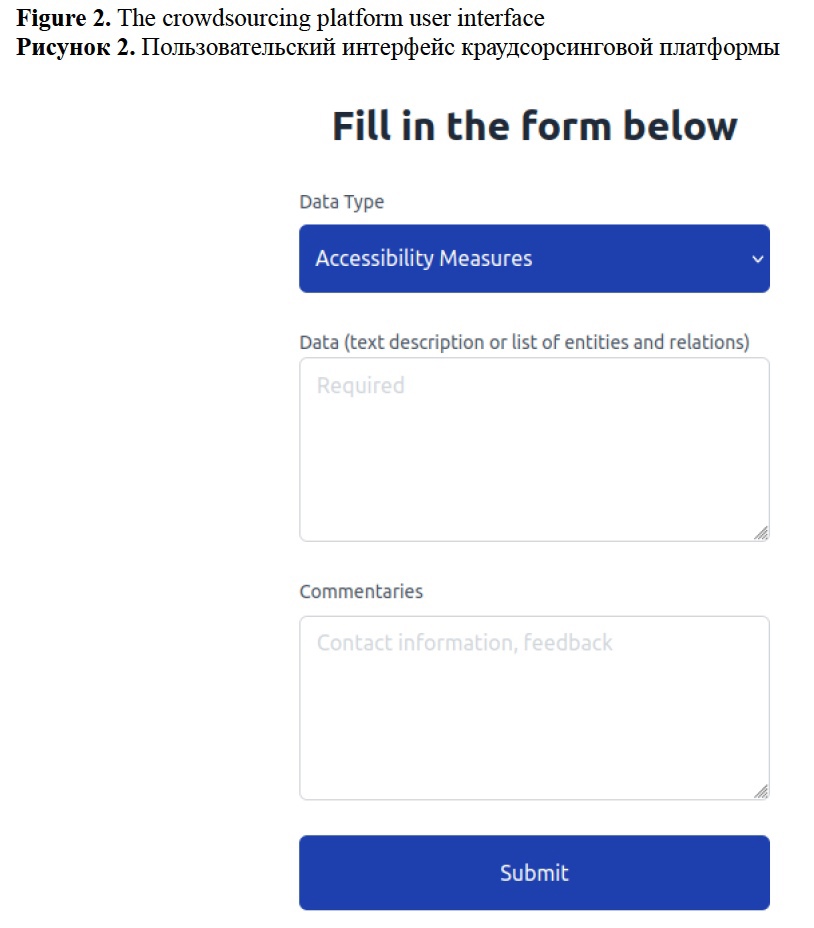
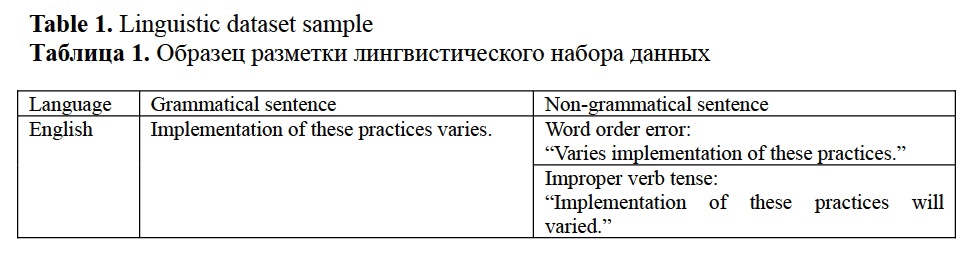
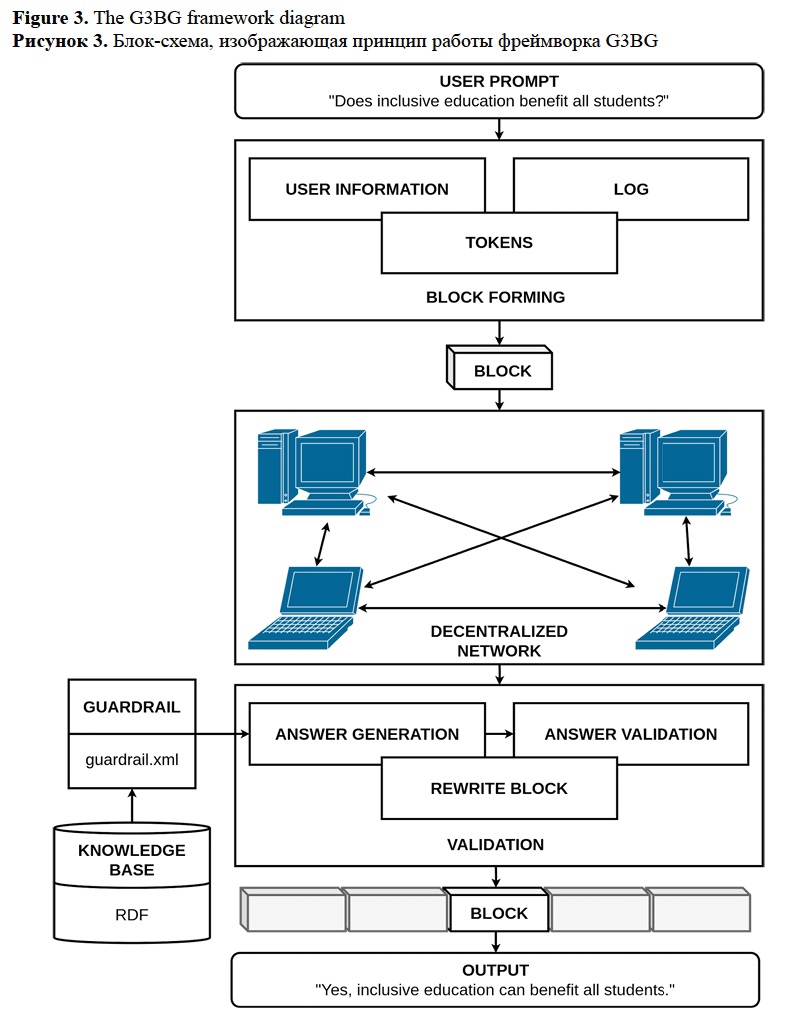



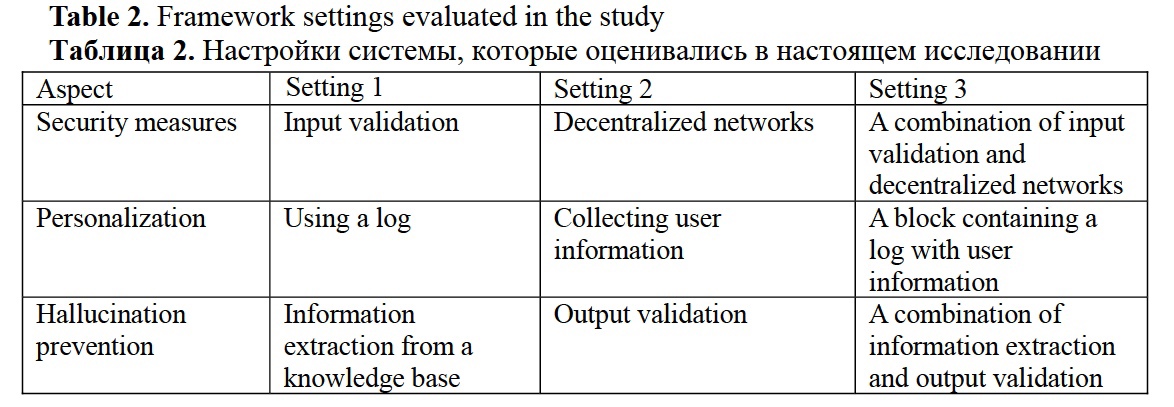



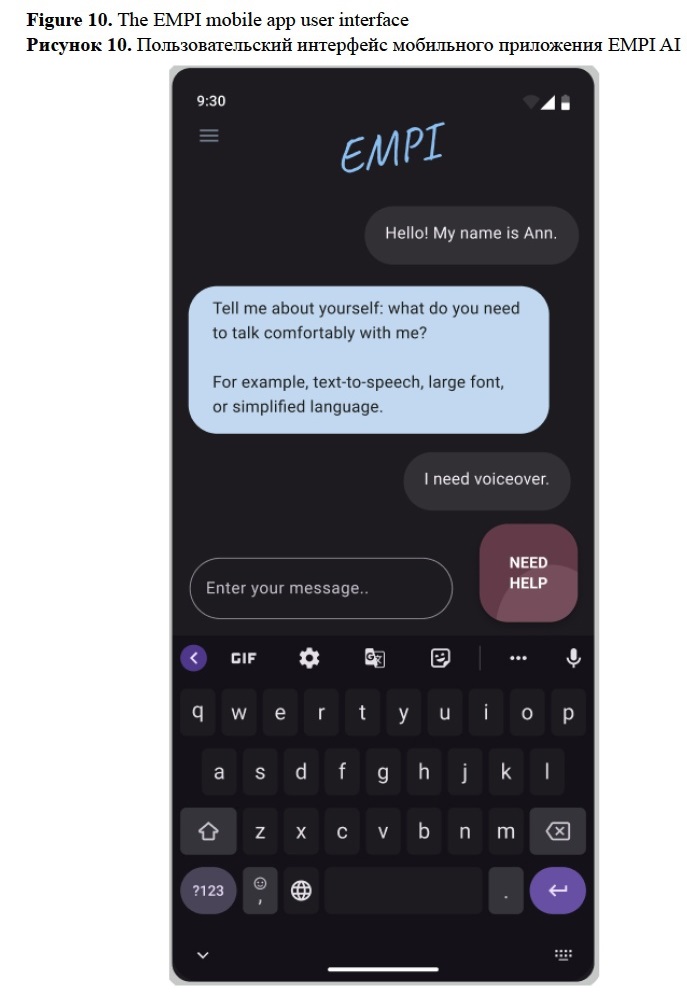
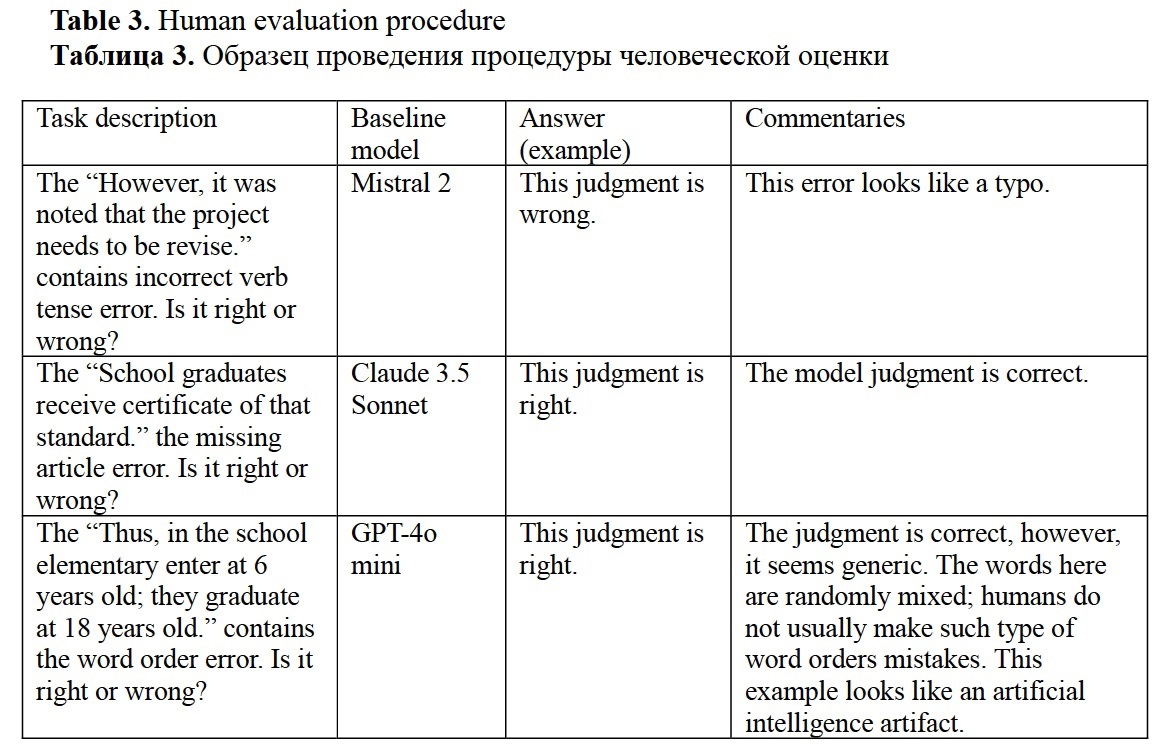
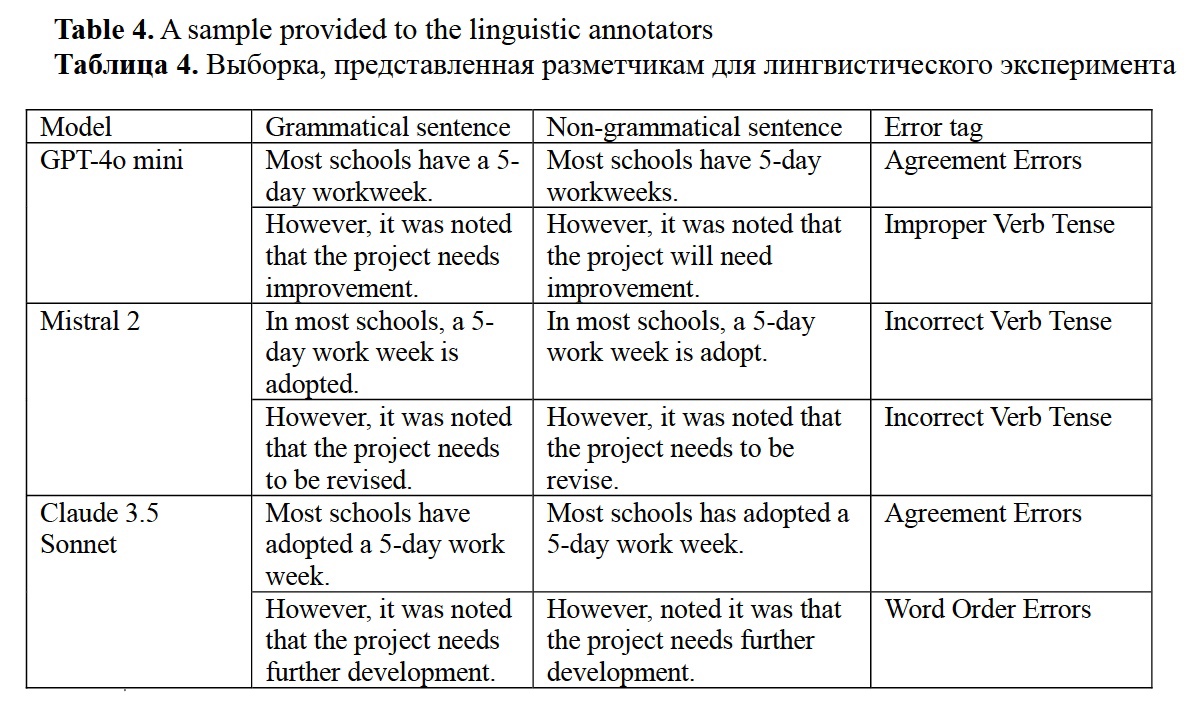
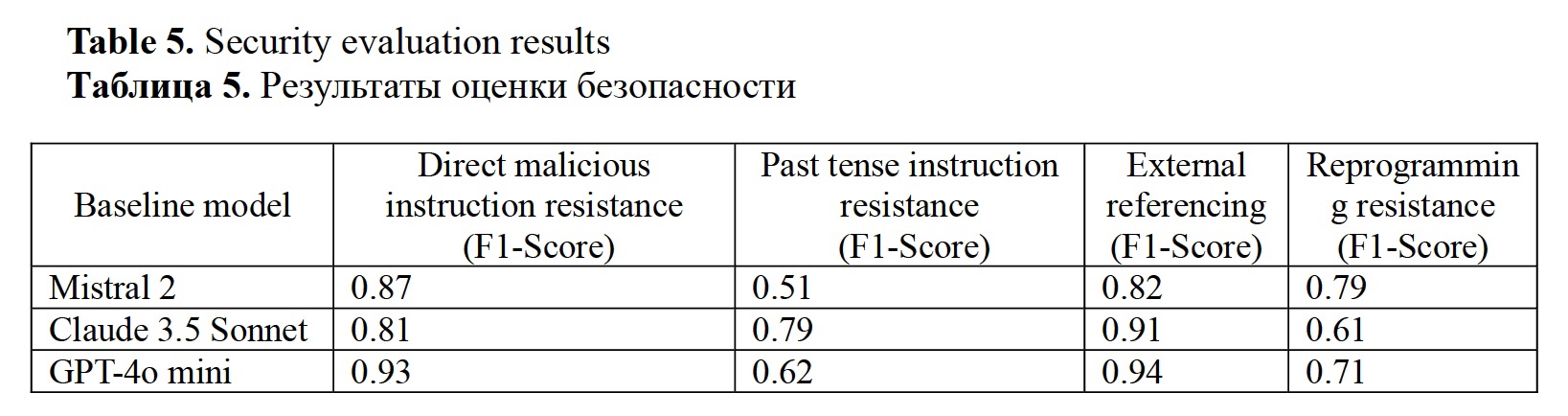
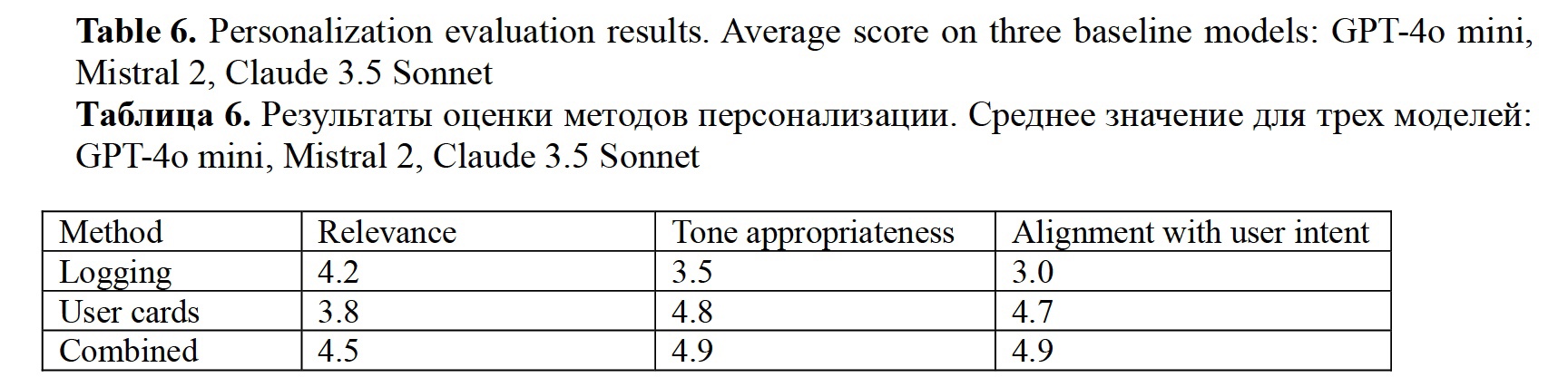
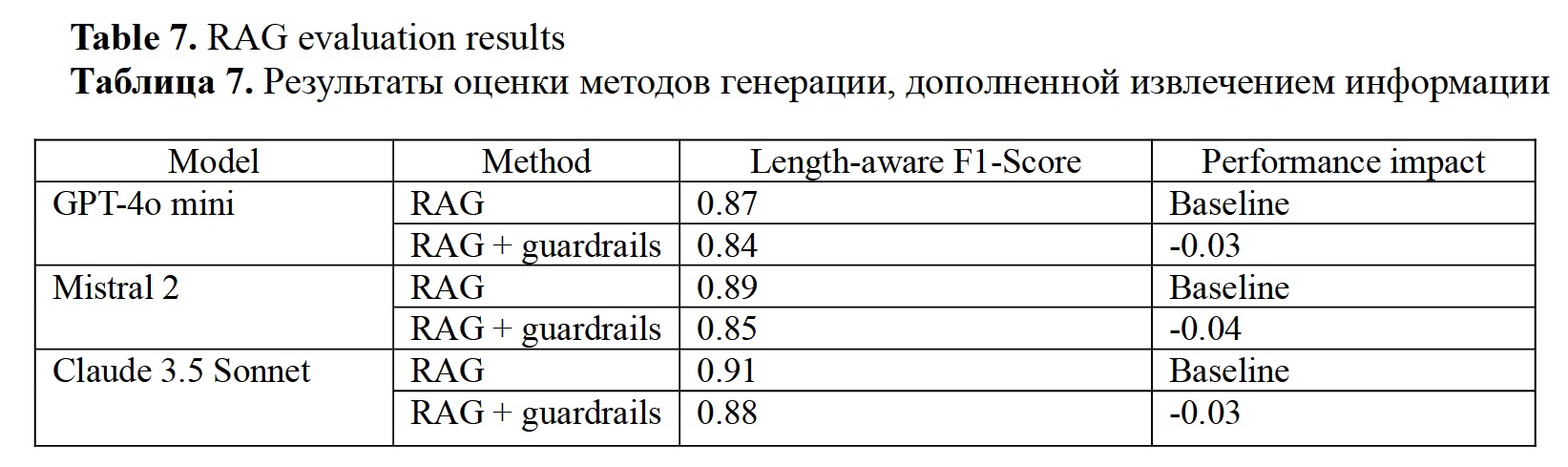

Firsanova, V. I. (2024). A graph-based approach to closed-domain natural language generation, Research Result. Theoretical and Applied Linguistics, 10 (3), 135-167.


















While nobody left any comments to this publication.
You can be first.
Andriushchenko, M. and Flammarion, N. (2024). Does Refusal Training in LLMs Generalize to the Past Tense? arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.11969. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2407.11969
Anthropic. (2024). Claude 3.5 Sonnet Model Card Addendum. [Online], available at: https://www-cdn.anthropic.com/fed9cc193a14b84131812372d8d5857f8f304c52/Model_Card_Claude_3_Addendum.pdf (Accessed 06 September 2024)
Ayyamperumal, S. G. and Ge, L. (2024). Current state of LLM Risks and AI Guardrails, arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.12934. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2406.12934
Choi, E., Jo, Y., Jang, J. and Seo, M. (2022). Prompt injection: Parameterization of fixed inputs, arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.11349. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2206.11349
Christiano, P. F., Leike, J., Brown, T., Martic, M., Legg, S. and Amodei, D. (2017). Deep reinforcement learning from human preferences, Advances in neural information processing systems, 30, 1–9. DOI: 10.5555/3294996.3295184
Dettmers, T., Pagnoni, A., Holtzman, A. and Zettlemoyer, L. (2024). QLoRA: Efficient finetuning of quantized LLMs, Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 36, 1–28. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2305.14314
Devlin, J., Chang, M. W., Lee, K. and Toutanova, K. (2018). BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding, arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1810.04805
Dong, Y., Mu, R., Jin, G., Qi, Y., Hu, J., Zhao, X., Meng, J., Ruan, W. and Huang, X. (2024). Building Guardrails for Large Language Models, arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.01822. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2402.01822
Firsanova, V. (2023). Towards building a mobile app for people on the spectrum, Companion Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023, 555–559. DOI: 10.1145/3543873.3587533
Firsanova, V. (2021). The advantages of human evaluation of sociomedical question answering systems, International Journal of Open Information Technologies, 12, 53–59. DOI: 10.25559/INJOIT.2307-8162.09.202112.53-59
Gage, P. (1994). A new algorithm for data compression, The C Users Journal, 12 (2), 23–38.
Gao, J., Galley, M. and Li, L. (2018). Neural approaches to conversational AI, The 41st international ACM SIGIR conference on research & development in information retrieval, 1371–1374. DOI: 10.1145/3209978.3210183
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y. and Courville, A. (2016). Deep learning, MIT press.
Google Cloud. (2024). Cloud Computing Services. [Online], available at: https://cloud.google.com/ (Accessed 06 September 2024)
Guu, K., Lee, K., Tung, Z., Pasupat, P. and Chang, M. (2020). Retrieval augmented language model pre-training, International conference on machine learning, 3929–3938.
Hendrycks, D., Burns, C., Basart, S., Zou, A., Mazeika, M., Song, D. and Steinhardt, J. (2020). Measuring massive multitask language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.03300. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2009.03300
Hewitt, J. and Manning, C. D. (2019). A structural probe for finding syntax in word representations, Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), 4129–4138. DOI: 10.18653/v1/N19-1419
Hu, E. J., Shen, Y., Wallis, P., Allen-Zhu, Z., Li, Y., Wang, S., Wang, L and Chen, W. (2021). LoRA: Low-rank adaptation of large language models, arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.09685. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2106.09685
Jacob, B., Kligys, S., Chen, B., Zhu, M., Tang, M., Howard, A., Adam, H. and Kalenichenko, D. (2018). Quantization and Training of Neural Networks for Efficient Integer-Arithmetic-Only Inference, arXiv preprint arXiv:1712.05877. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1712.05877
Jelinek, F., Mercer, R. L., Bahl, L. R. and Baker, J. K. (1977). Perplexity – a measure of the difficulty of speech recognition tasks, The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 62 (S1), S63–S63.
Ji, Z., Lee, N., Frieske, R., Yu, T., Su, D., Xu, Y., Ishii, E., Bang, Y., Chen, D., Dai, W., Chan, H. S., Madotto, A. and Fung, P. (2023). Survey of hallucination in natural language generation, ACM Computing Surveys, 55 (12), 1–38.
Jiang, A. Q., Sablayrolles, A., Mensch, A., Bamford, C., Chaplot, D. S., Casas, D. D. L., Bressand, F., Lengyel, G., Lample, G., Saulnier, L. and Lavaud, L.R. (2023). Mistral 7B, arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.06825. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2310.06825
Jurafsky, D. and Martin, J. H. (2023). Speech and language processing: An introduction to natural language processing, computational linguistics, and speech recognition, Stanford University, University of Colorado at Boulder.
LM Studio. (2024). LM Studio Documentation. [Online], available at: https://lmstudio.ai/docs/welcome (Accessed 06 September 2024).
Luo, H., Luo, J. and Vasilakos, A. V. (2023). BC4LLM: Trusted artificial intelligence when blockchain meets large language models, arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.06278. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2310.06278
McCarthy, J. (1987). Generality in artificial intelligence, Communications of the ACM, 30 (12), 1030–1035.
Meister, C., Cotterell, R. (2021). Language Model Evaluation Beyond Perplexity, Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), 5328–5339.
Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G. and Dean, J. (2013). Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space, arXiv preprint arXiv:1301.3781. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1301.3781
Mistral. (2024). Mistral Large 2. [Online], available at: https://mistral.ai/news/mistral-large-2407/ (Accessed 06 September 2024)
Morris, J., Hirst, G. (1991). Lexical Cohesion Computed by Thesaural relations as an indicator of the structure of text, Computational Linguistics, 17 (1), 21–48.
OpenAI. (2024). GPT-4o mini: advancing cost-efficient intelligence. [Online], available at: https://openai.com/index/gpt-4o-mini-advancing-cost-efficient-intelligence/ (Accessed 06 September 2024)
OpenAI API. (2024). Open AI API. [Online], available at: https://openai.com/index/openai-api (Accessed 06 September 2024)
Ouyang, L., Wu, J., Jiang, X., Almeida, D., Wainwright, C., Mishkin, P., Zhang, C., Agarwal, S., Slama, K., Ray, A. and Schulman, J. (2022). Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback, Advances in neural information processing systems, 6 (35), 27730–27744. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2203.02155
Polyzotis, N. and Zaharia, M. (2021). What can data-centric AI learn from data and ML engineering? arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.06439. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2112.06439
Priest, G. (2000). Logic: A Very Short Introduction, Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK.
Raffel, C., Shazeer, N., Roberts, A., Lee, K., Narang, S., Matena, M., Zhou, Y., Li, W. and Liu, P. J. (2020). Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer, Journal of machine learning research, 21 (140), 1–67.
Rajpurkar, P., Zhang, J., Lopyrev, K. and Liang, P (2016). SQuAD: 100,000+ questions for machine comprehension of text, arXiv preprint arXiv:1606.05250. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1606.05250
Rajpurkar, P., Jia, R. and Liang, P. (2018). Know what you don't know: Unanswerable questions for SQuAD, arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.03822. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1806.03822
Ruder, S. (2019). Neural transfer learning for natural language processing, NUI Galway.
Schmidhuber, J. (1987). Evolutionary principles in self-referential learning, or on learning how to learn: the meta-meta-... hook, Technische Universität München.
Talmor, A, Herzig, J, Lourie, N. and Berant, J. (2018). Commonsenseqa: A question answering challenge targeting commonsense knowledge, arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.00937. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1811.00937
Thakur, N., Reimers, N., Rücklé, A., Srivastava, A. and Gurevych, I. (2021). Beir: A heterogenous benchmark for zero-shot evaluation of information retrieval models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.08663. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2104.08663bs/2104.08663
Van Rijsbergen, P. J. (1979). InformationRetrieval, London: Butterworths.
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A. N., Kaiser, Ł. and Polosukhin, I. (2017). Attention is all you need, Advances in neural information processing systems, 30, 261–272. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1706.03762
Wolf, T., Debut, L., Sanh, V., Chaumond, J., Delangue, C., Moi, A., Cistac, P., Rault, T., Louf, R., Funtowicz, M. and Davison, J. (2019). HuggingFace's Transformers: State-of-the-art natural language processing, arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.03771. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1910.03771
Zhang, P., Xiao, S., Liu, Z., Dou, Z. and Nie, J. Y. (2023). Retrieve anything to augment large language models, arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.07554. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2310.07554
Zhong, W., Cui, R., Guo, Y., Liang, Y., Lu, S., Wang, Y., Saied, A., Chen, W. and Duan, N. (2023). AGIEval: A human-centric benchmark for evaluating foundation models, arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.06364. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2304.06364