Revealing Cultural Meaning with Trilingual Embeddings: A New Audit of LLM Multilingual Behavior
Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly regarded as authoritative mediators of multilingual meaning; however, their ability to preserve culturally grounded lexical distinctions remains uncertain. This issue is especially critical for the core lexicon – high-frequency, culturally salient words that constitute the conceptual foundation of linguistic cognition within a community. If these foundational meanings are distorted, the resulting semantic shifts can propagate through downstream tasks, interpretations, and educational applications. Despite this risk, robust methods for evaluating LLM fidelity to culturally embedded lexical semantics remain largely undeveloped. This editorial introduces a novel diagnostic approach based on trilingual aligned word embeddings for Russian, Lingala, and French. By aligning embeddings into a shared distributional space, we obtain an independent semantic reference that preserves the internal structure of each language. French serves as a high-resource pivot, enabling comparisons without forcing the low-resource language into direct competition with English or Russian embedding geometries.
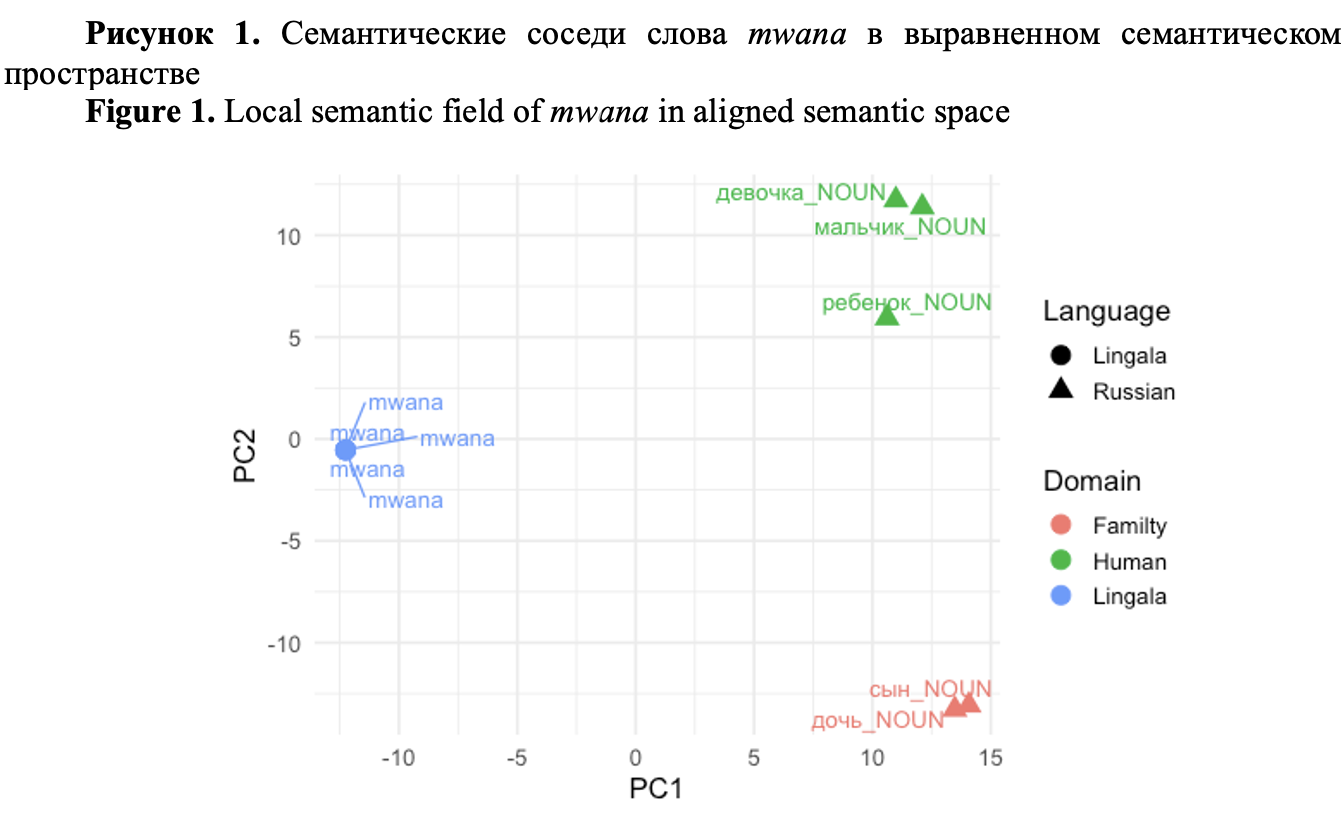
We examine several culturally central lexical items – including kinship and evaluative terms – to illustrate how an aligned manifold can reveal potential points of semantic tension between LLM outputs and corpus-grounded meanings. While our case studies do not claim to expose fully systematic biases, they demonstrate how the proposed framework can uncover subtle discrepancies in meaning representation and guide a more comprehensive investigation.
We argue that embedding-based diagnostics provide a promising foundation for auditing the behavior of multilingual LLMs, particularly for low-resource languages whose semantic categories risk being subsumed under English-centric abstractions. This work outlines a research trajectory rather than a completed map and calls for deeper, community-centered efforts to safeguard linguistic and cultural specificity in the age of generative AI.
Figures

Litvinova, T. A., Dekhnich, O. V. (2025). Revealing cultural meaning with trilingual embeddings: a new audit of LLM multilingual behavior, Research Result. Theoretical and Applied Linguistics, 11 (4), 4–23.


















While nobody left any comments to this publication.
You can be first.
Artetxe, M., Labaka, G. and Agirre, E. (2018). A robust self-learning method for fully unsupervised cross-lingual mappings of word embeddings, Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), 789–798. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P18-1073(In English).
Bird, S. (2020). Decolonising speech and language technology, in Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, 3504–3519, Barcelona, Spain (Online). International Committee on Computational Linguistics. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.coling-main.313(In English).
Blasi, D. E., Anastasopoulos, A. and Neubig, G. (2022). Systematic inequalities in language technology performance across the world’s languages, Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Volume 1: Long Papers, 5486–5505, May 22-27, 2022. DOI: 10.18653/v1/2022.acl-long.376 (In English).
Goddard, C. and Wierzbicka, A. (2014). Words and meanings: Lexical semantics across domains, languages, and cultures, Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199668434.001.0001(In English).
Guo, Y., Conia, S., Zhou, Z., Li, M., Potdar, S. and Xiao, H. (2024). Do Large Language Models Have an English Accent? Evaluating and Improving the Naturalness of Multilingual LLMs, Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics.https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2410.15956(In English).
Joshi, P., Santy, S., Budhiraja, A., Bali, K. and Choudhury, M. (2020). The state and fate of linguistic diversity in the NLP world, Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online. Association for Computational Linguistics., 6282–6293. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.acl-main.560(In English).
Li, C., Chen, M., Wang, J., Sitaram, S. and Xie, X. (2024). CultureLLM: incorporating cultural differences into large language models, in Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS '24), Vol. 37. Curran Associates Inc., Red Hook, NY, USA, Article 2693, 84799–84838. https://doi.org/10.52202/079017-2693(In English).
Litvinova, T. A., Mikros, G. K. and Dekhnich, O. V. (2024). Writing in the era of large language models: a bibliometric analysis of research field. Research Result, Theoretical and Applied Linguistics, 10 (4), 5–16. https://doi.org/10.18413/2313-8912-2024-10-4-0-1(In English)
Liu, H., Cao, Y., Wu, X., Qiu, C., Gu, J. et al. (2025). Towards realistic evaluation of cultural value alignment in large language models: Diversity enhancement for survey response simulation, Information Processing and Management, 62, 4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2025.104099 (In English).
Malt, B. C and Majid, A. (2013). How thought is mapped into words, Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci. Nov; 4 (6), 583–597. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcs.1251(In English).
Masoud, R., Liu, Z., Ferianc, M., Treleaven, P. C. and Rodrigues, M. (2025). Cultural Alignment in Large Language Models: An Explanatory Analysis Based on Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions, in Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Computational Linguistics, 8474–8503, Abu Dhabi, UAE, Association for Computational Linguistics. https://aclanthology.org/2025.coling-main.567/(In English).
Mikolov, T., Chen, K., Corrado, G. and Dean, J. (2013). Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space, in 1st International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2013, Scottsdale, Arizona, USA, May 2-4, 2013, Workshop Track Proceedings, 2013. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1301.3781(In English).
Mirko, F. and Lavazza, A. (2025), English in LLMs: The Role of AI in Avoiding Cultural Homogenization, in Philipp Hacker (ed.), Oxford Intersections: AI in Society (Oxford, online edn, Oxford Academic, 20 Mar. 2025). https://doi.org/10.1093/9780198945215.003.0140(In English).
Pistilli, G., Leidinger, A., Jernite, Y., Kasirzadeh, A., Luccioni, A. S. and Mitchell, M. (2024). CIVICS: Building a Dataset for Examining Culturally-Informed Values in Large Language Models. Proceedings of the AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society, 7 (1), 1132-1144. https://doi.org/10.1609/aies.v7i1.31710(In English).
Qin, L., Chen, Q., Zhou, Y., Chen, Z., Li, Y., Liao, L., Li, M., Che, W., Yu, P. S. (2025). A survey of multilingual large language models, Patterns, 6 (1), 101118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patter.2024.101118(In English).
Ruder, S., Vulić, I. and Søgaard, A. (2019). A survey of cross-lingual word embedding models, Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 65, 569–631. https://doi.org/10.1613/jair.1.11640(In English).
Wendler, C., Veselovsky, V., Monea, G. and West, R. (2024). Do Llamas Work in English? On the Latent Language of Multilingual Transformers, in Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), 15366–15394, Bangkok, Thailand. Association for Computational Linguistics. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2024.acl-long.820(In English).
Wierzbicka, A. M. (1996). Semantics: Primes and Universals, Oxford University Press, UK. (In English).
Xing, C., Wang, D., Liu, C. and Lin, Y. (2015). Normalized word embedding and orthogonal transform for bilingual word translation, in Proceedings of the 2015 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, 1006–1011, Denver, Colorado. Association for Computational Linguistics. https://doi.org/10.3115/v1/N15-1104(In English).
Tatiana A. Litvinova acknowledges the support of the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation (the research was supported by the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation within the framework of the state assignment in the field of science, topic number QRPK-2025-0013). Olga V. Dekhnich received no financial support for the research, authorship, and publication of this article.