How Environmental Activists Persuade: A Multimodal Speech Act Approach
Given the rising prominence of youth climate activists in global discourse and the lack of research on how they persuade multimodally, this study examines the integration of speech acts and gestures in their rhetoric. By bridging speech act theory and gesture analysis, the research explores an underexplored aspect of persuasive communication in environmental activism. Analyzing 1230 speech acts from prominent activists Greta Thunberg, Jamie Margolin, and Xiye Bastida, the research applies Aristotle’s rhetorical triad (ethos, pathos, logos) and Searle’s taxonomy of illocutionary acts to elucidate the strategic alignment of multimodal components with persuasive intent. Among the speech acts, 172 multimodal units (gesture – verbal couplings) were identified and classified into detailed multimodal categories, highlighting dominant uses of pragmatic and discourse-structuring gestures alongside varied facial expressions and postures. These couplings were categorized by function as follows: structuring discourse (n=51) emerged as the most frequent, followed by pragmatic functions (n=44), formulating thoughts (n=27), object-representing gestures (n=29), and action-representing gestures (n=21). Results indicate a predominance of emotional (pathos) and ethical (ethos) appeals reinforced through pragmatic gestures and expressive mimicry, with representational gestures less frequent but strategically significant. This multimodal integration confirms that persuasive efficacy in activist discourse is significantly enhanced by embodied, contextually sensitive communication practices. The findings underline the necessity of expanded analytical models in multimodal pragmatics, supporting future research directions integrating quantitative gesture analysis and advanced coding methodologies.
Figures
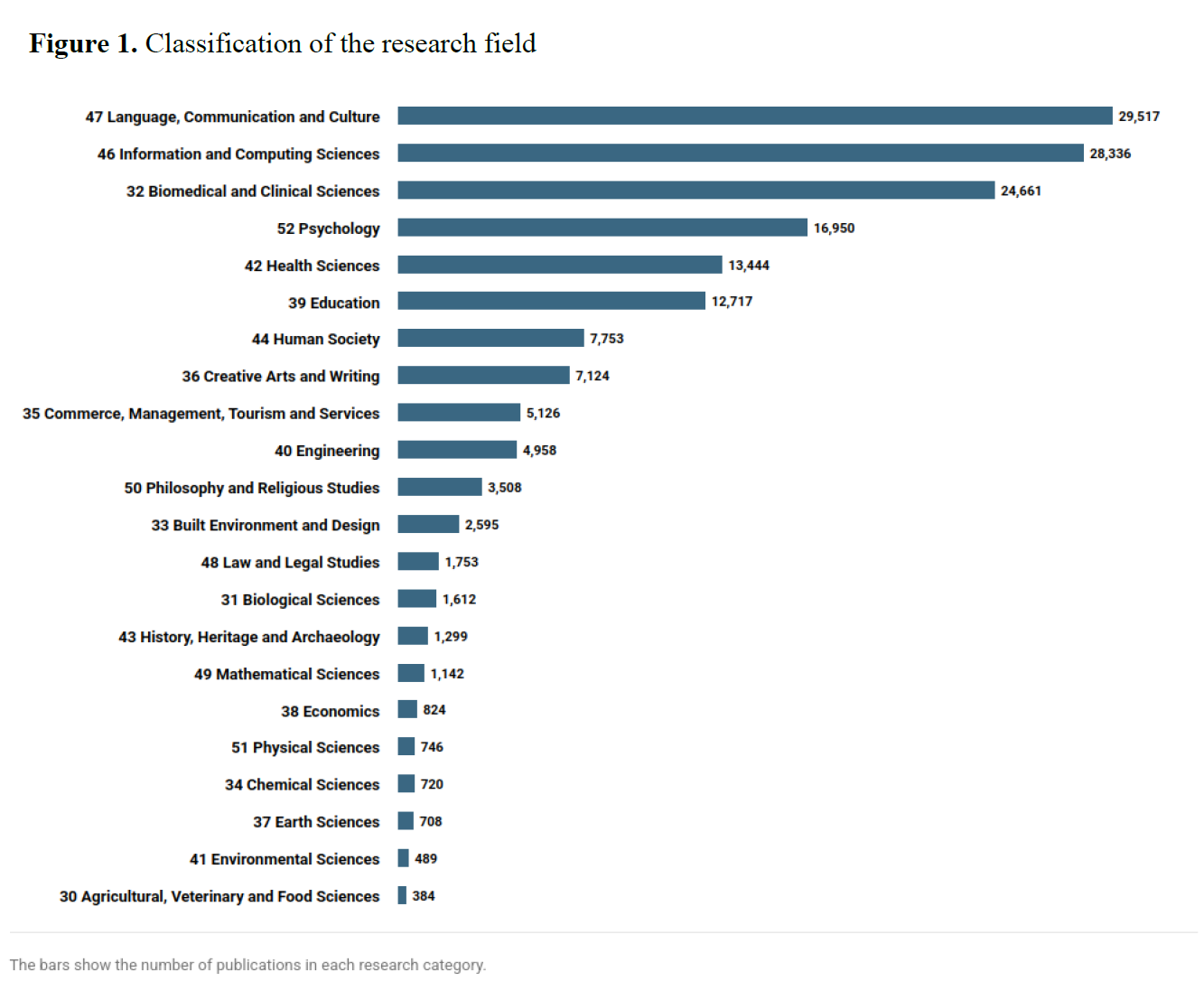
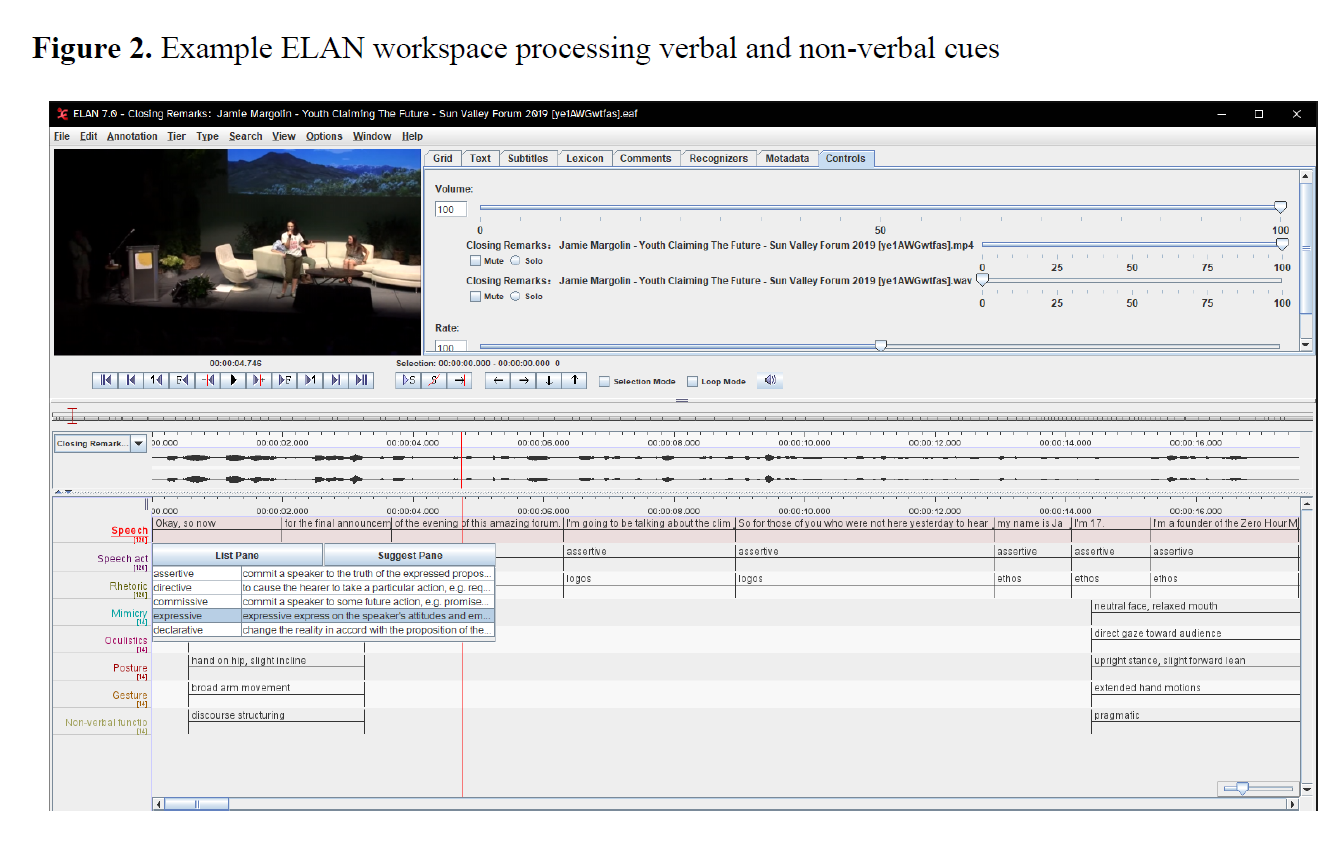

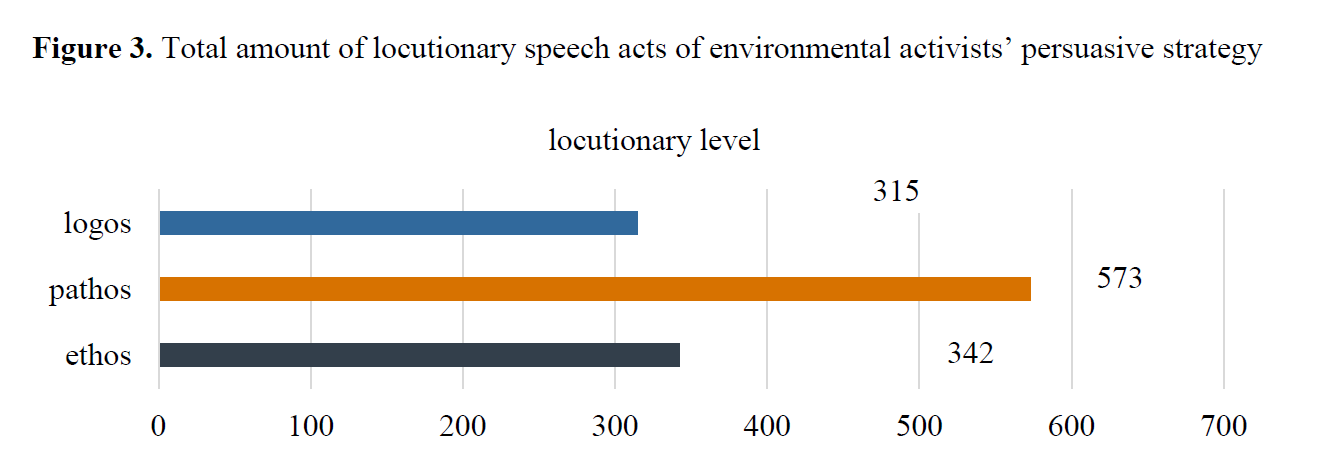
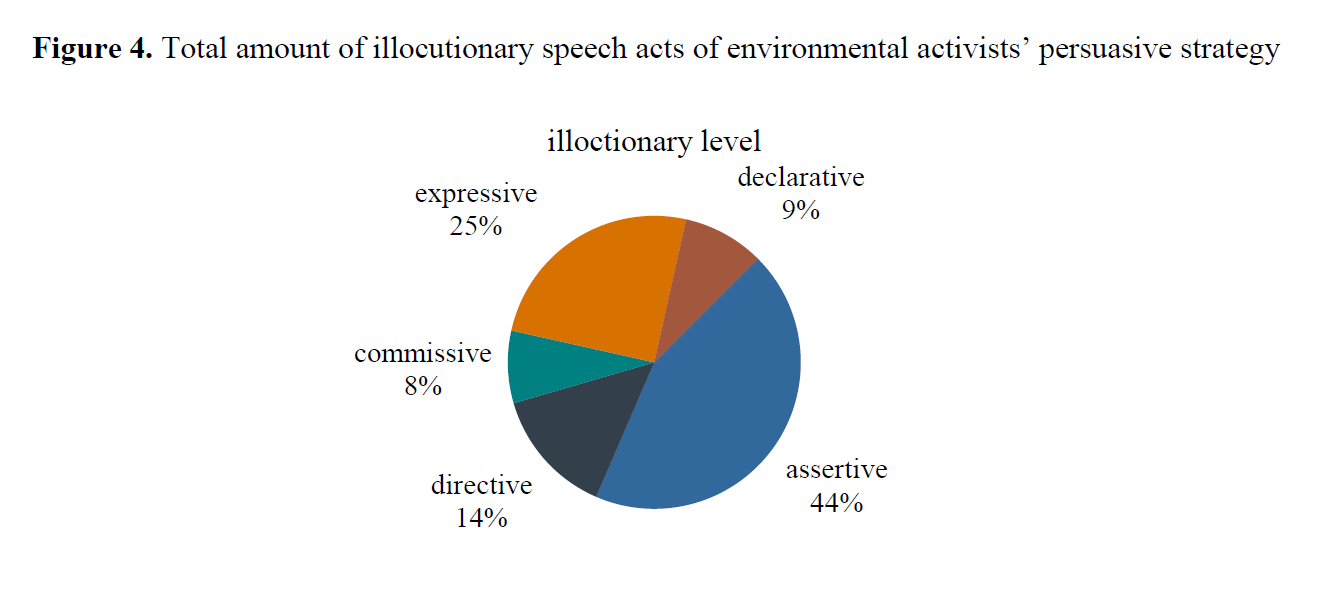




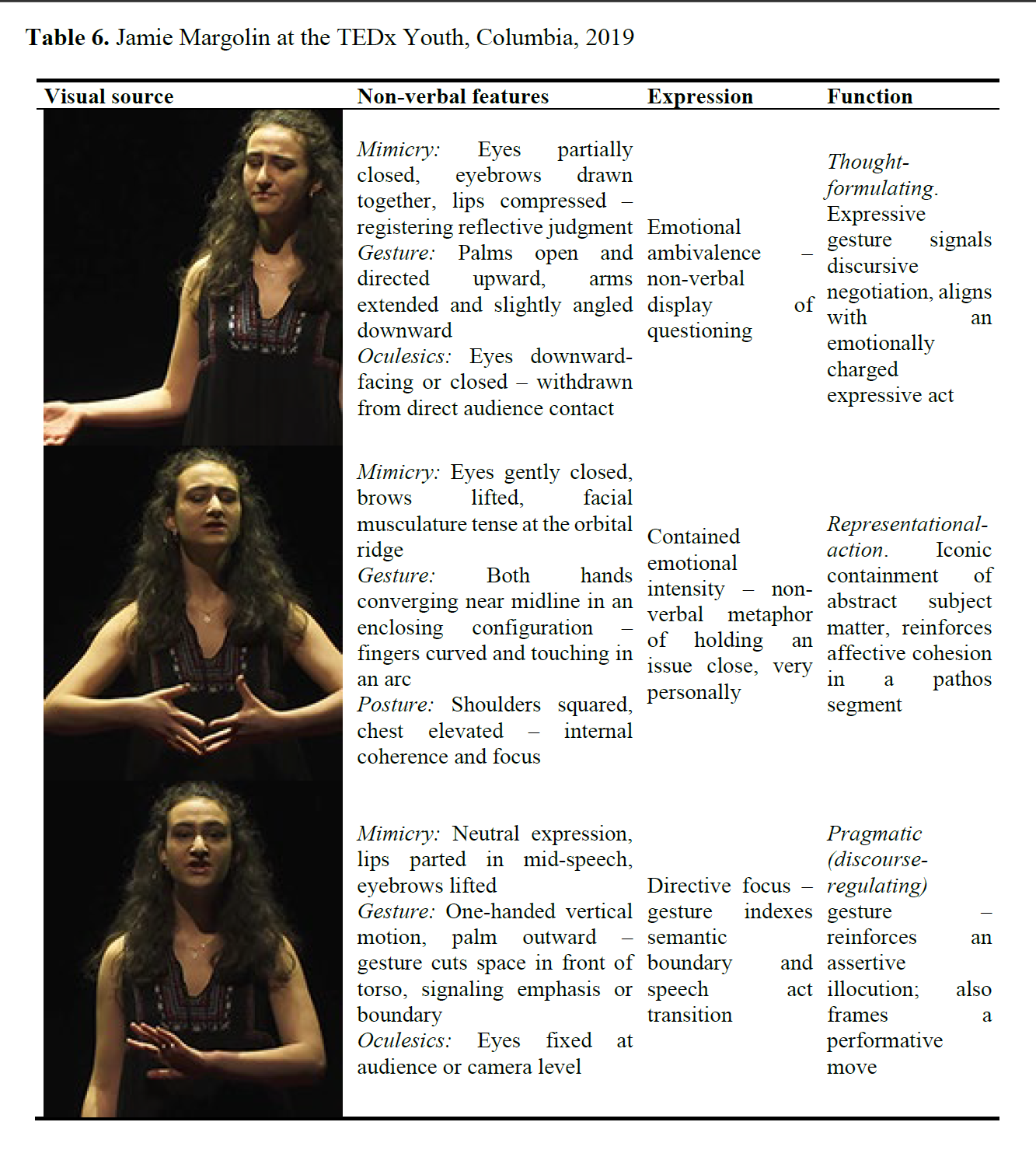



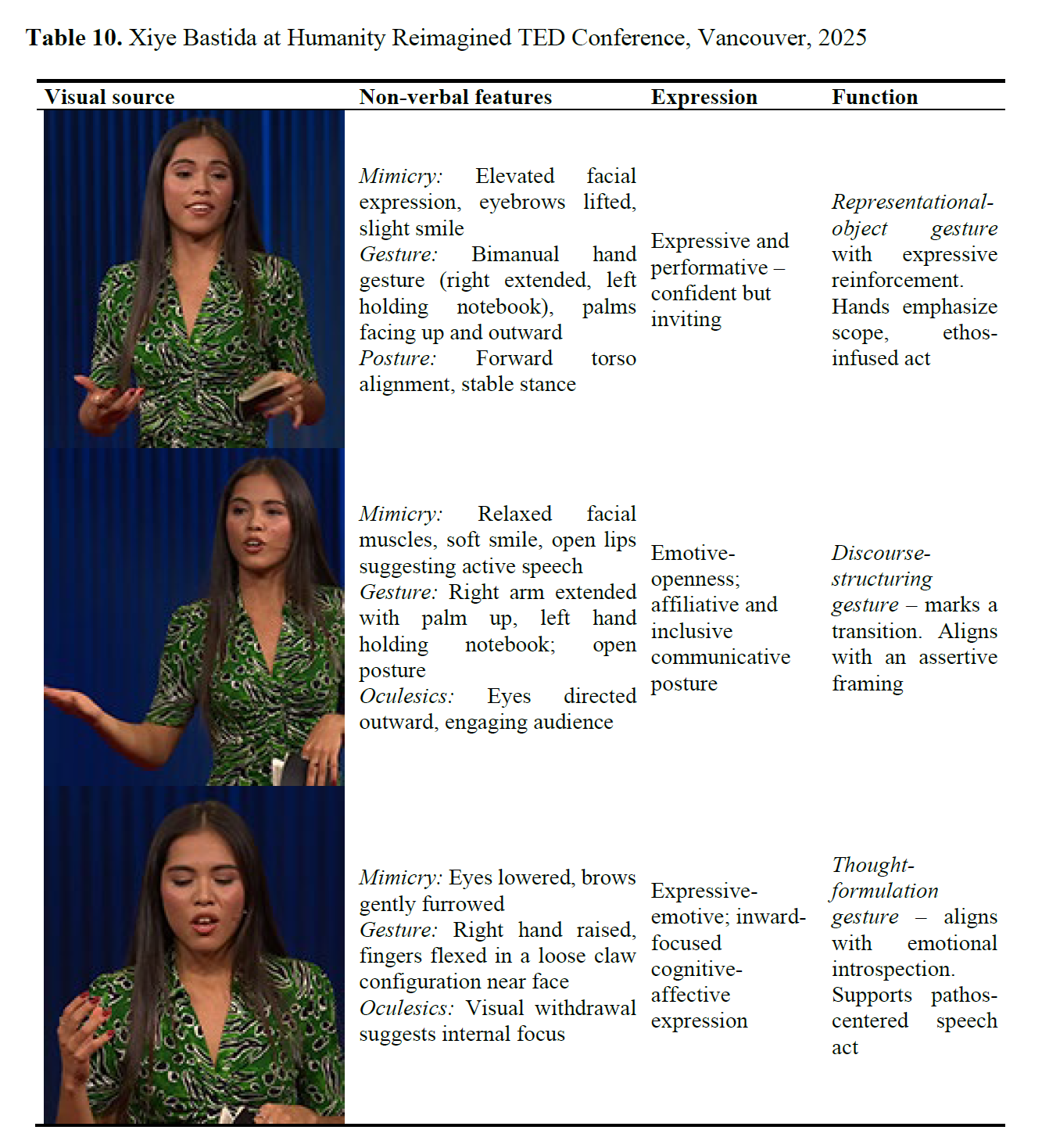
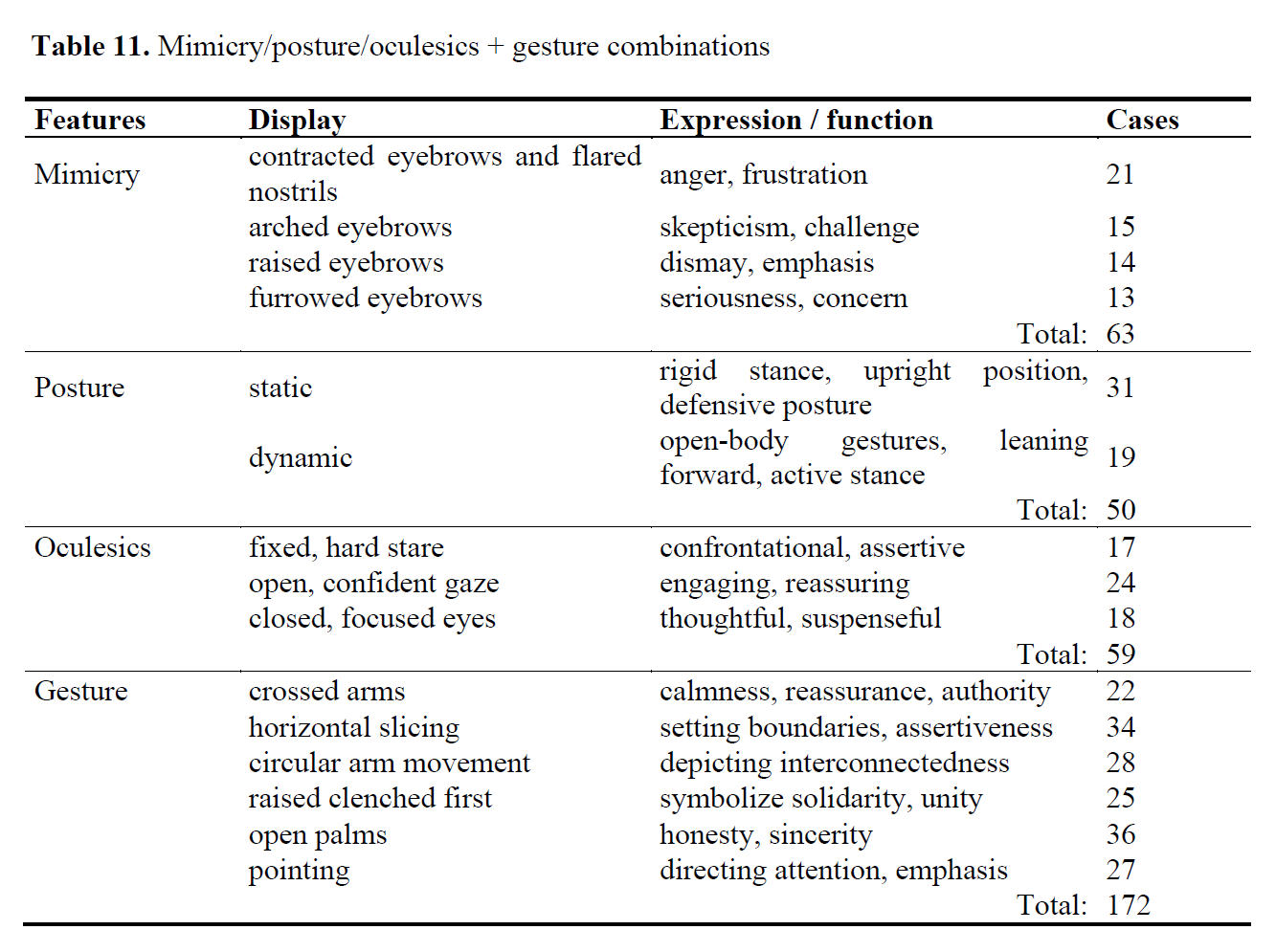
Murugova, E., Khodyka, A. (2025). How Environmental Activists Persuade: A Multimodal Speech Act Approach, Research Result. Theoretical and Applied Linguistics, 11 (4), 85–118.


















While nobody left any comments to this publication.
You can be first.
Abercrombie, D. (1968). Paralanguage, British Journal of Disorders of Communication, 3 (1), 55–59. https://doi.org/10.3109/13682826809011441(In English)
Barrero Salinas, A. F. (2023). J. L. Austin and John Searle on Speech Act Theory, The Collector, available at: www.thecollector.com/speech-act-theory-austin-and-searle (Accessed 28 June 2025) (In English)
Beltrán-Planques, V. and Querol-Julián, M. (2018). English language learners’ spoken interaction: What a multimodal perspective reveals about pragmatic competence, System, 77, 80–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2018.01.008(In English)
Birdwhistell, R. L. (2021). Introduction to Kinesics: An Annotation System for Analysis of Body Motion and Gesture, Hassell Street Press. (In English)
Bouchey, B., Castek, J. and Thygeson, J. (2021). Multimodal learning, SpringerBriefs in statistics, 35–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58948-6_3(In English)
Brügger, A., Gubler, M., Steentjes, K. and Capstick, S. B. (2020). Social identity and risk perception explain participation in the Swiss youth climate strikes, Sustainability, 12 (24), 10605. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122410605(In English)
Bucher, H. (2025). Insights into the black box of multimodal meaning-making: investigating the reception of multimodality empirically, Visual Communication, 24 (3), 543–569. https://doi.org/10.1177/14703572251335833(In English)
Cambria, E. (2025). Pragmatics Processing, in Understanding Natural Language Understanding, Springer, 55–77. https://doi.org///10.1007/978-3-031-73974-3_4(In English)
Campoy-Cubillo, M. C. and Querol-Julián, M. (2021). Assessing multimodal listening comprehension through online informative videos: The operationalisation of a new listening Framework for ESP in Higher Education, in Multimodality in English Language Learning, 238–256. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003155300-17(In English)
Cienki, A. (2013). Gesture, Space, Grammar, and Cognition, in Auer, P., Hilpert, M., Stukenbrock, A., Szmrecsanyi, B. (eds.) Space in Language and Linguistics, De Gruyter, 667–686. (In English)
Cornelio, G. S., Martorell, S. and Ardèvol, E. (2024). "My goal is to make sustainability mainstream": emerging visual narratives on the environmental crisis on Instagram, Frontiers in Communication, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcomm.2023.1265466(In English)
Cox, R. (2013). Environmental Communication and the Public Sphere, SAGE. (In English)
Crible, L. and Kosmala, L. (2025). Multimodal pragmatic markers of feedback in dialogue. Languages, 10 (6), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/languages10060117(In English)
Dicerto, S. (2018). Multimodal Meaning in Context: Pragmatics, in Multimodal Pragmatics and Translation: A New Model for Source Text Analysis, Springer, 37–59, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-69344-6_3(In English)
Doyle, J. (2012). Here Today: Thoughts on Communicating Climate Change, available at: https://cris.brighton.ac.uk/ws/portalfiles/portal/21389609/HereTodayThoughtsOnCommunicatingClimateChange_JulieDoyle.pdf (Accessed 28 June 2025) (In English)
Duchak, O. (2014): Visual literacy in educational practice, Czech-Polish Historical and Pedagogical Journal, 6/2, 41–48. DOI: 10.2478/cphpj-2014-0017 (In English)
Ekman, P. and Friesen, W. (1971). Constants across Cultures in the Face and Emotion, Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 17 (2), 124–129. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0030377(In English)
Enfield, N. J. (2009). The Anatomy of Meaning: Speech, Gesture, and Composite Utterances, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511576737(In English)
Fang, Y. (2023). Review of Corpus Pragmatics, Corpus Pragmatics, 7, 401–404. DOI: 10.1007/S41701-023-00149-8(In English)
Freigang, F., Klett, S. and Kopp , S. (2017). Pragmatic Multimodality: Effects of Nonverbal Cues of Focus and Certainty in a Virtual Human, in Intelligent Virtual Agents, Springer, 142–155, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67401-8_16(In English)
Goodwin, C. (2017). Co-Operative Action. Learning in Doing: Social, Cognitive and Computational Perspectives, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781139016735(In English)
Haryanti, P., Saddhono, K. and Anindyarini, A. (2023). Multimodal as a New Perspective in Pragmatics in the Digital Era: Literature Review. International Conference of Humanities and Social Science (ICHSS), 494–501, available at: https://www.programdoktorpbiuns.org/index.php/proceedings/article/view/319 (Accessed 28 June 2025) (In English)
Hömke, P., Holler, J. and Levinson, S. C. (2018). Eye blinks are perceived as communicative signals in human face-to-face interaction, PLoS ONE, 13 (12), e0208030. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0208030(In English)
Huang, L. (2021). Toward Multimodal Corpus Pragmatics: Rationale, Case, and Agenda. Digital Scholarship in the Humanities, 36, 101–114, https://doi.org/10.1093/llc/fqz080(In English)
Interaction Design Foundation — IxDF (2016). The Persuasion Triad – Aristotle Still Teaches, available at: https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/the-persuasion-triad-aristotle-still-teaches (Accessed 28 June 2025) (In English)
Iriskhanova, O. K. (2022). Multimodal Discourse Study, Studia Philologica, Moscow, Russia. (In Russian)
Jewitt, C. (ed.) (2023). The Routledge Handbook of Multimodal Analysis, 2nd ed., Routledge. (In English)
Jewitt, C. (2006). Technology, Literacy, and Learning: A Multimodal Approach, Routledge. (In English)
Kendon, A. (2004). Gesture: Visible Action as Utterance, Cambridge UK. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511807572(In English)
Kendrick, K. H. (2015). The intersection of turn-taking and repair: the timing of other-initiations of repair in conversation, Frontiers in Psychology, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00250(In English)
Kibrik, A. and El’bert, E. (2008). Understanding Spoken Discourse: The Contribution of Three In-formation Channels. Third International Conference on Cognitive Science, IP RAN, 82–84, available at: https://iling-ran.ru/kibrik/Information_channels@CogSci2008.pdf (Accessed 28 June 2025) (In English)
Kress, G. (2009). Multimodality: A Social Semiotic Approach to Contemporary Communica-tion. Routledge. (In English)
Landis, J. R. and Koch, G. G. (1977). The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics, 33 (1), 159–174. https://doi.org/10.2307/2529310(In English)
Lei, H. and Zhang, L. (2022). Development and Application of a Multimodal Corpus for Learn-ers’ Pragmatic Competence, Southern African Linguistics and Applied Language Studies, 40, 378–380. https://doi.org/10.2989/16073614.2022.2037443(In English)
Levinson, S. C. (2016). Speech acts, in The Oxford Handbook of Pragmatics, Oxford University Press eBooks. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199697960.013.22(In English)
Lim, F. V. (2020). Designing Learning with Embodied Teaching, Routledge eBooks. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429353178(In English)
Loos, C., German, A. and Meier, R. P. (2022). Simultaneous structures in sign languages: Acquisition and emergence, Frontiers in Psychology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.992589(In English)
Machin, D. and Mayr, A. (2012). How to Do Critical Discourse Analysis: A Multimodal Introduction, Sage Publications. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781036212933(In English)
McNeill, D. (1992). Hand and Mind: What Gestures Reveal about Thought, The University of Chicago Press. (In English)
Miller, L. B. (2025). From Persuasion Theory to Climate Action: Insights and Future Directions for Increasing Climate-Friendly Behavior, Sustainability, 17 (7), 2832. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17072832(In English)
Morell, T. (2018). Multimodal competence and effective interactive lecturing, System, 77, 70–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2017.12.006(In English)
Müller, C. (1998). Speech Related Gestures: History, Culture, Theory of Language, Berliner Wissenschafts-Verlag. (In German)
Müller, C., Cienki, A., Fricke, E., Ladewig, S., McNeill, D., Bressem, J. (2023). Body – Language – Communication: An International Handbook on Multimodality in Human Interaction, De Gruyter Mouton. (In English)
Norris, Si (ed.) (2012). Multimodality in Practice: Investigating Theory-in-Practice through. Methodology, Routledge Studies in Multimodality Book Series. (In English)
Norte Fernández-Pacheco, N. (2016). The orchestration of modes and EFL audio-visual comprehension: A multimodal discourse analysis of vodcasts. Dialnet, available at: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/dctes?codigo=59286 (Accessed 28 June 2025) (In English)
O’Callaghan, K. A., Nunn, P. D., Casey, S., Crimmins, G. and Dugmore, H. (2025). Speaking of climate change: Reframing effective communication for greater impact, Climate, 13 (4), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli13040069(In English)
Pflaeging, J and Stöckl, H. (2021). The Rhetoric of Multimodal Communication, Visual Communication, 20 (3), 319–26. https://doi.org/10.1177/14703572211010200(In English)
Rapp, C. (2023). Aristotle’s Rhetoric. The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, edited by Edward N. Zalta and Uri Nodelman, available at: https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/aristotle-rhetoric (Accessed 28 June 2025) (In English)
Russell, J. A. (1995). Facial expressions of emotion: What lies beyond minimal universality? Psychological Bulletin, 118 (3), 379–391. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.118.3.379(In English)
Searle, J. R. (1969). Speech acts,
Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9781139173438(In English)
Sidiropoulou, M. (2020). Understanding Migration through Translating the Multimodal Code, Journal of Pragmatics, 170, 284–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pragma.2020.09.020(In English)
Tindale, C. W. (2004). Rhetorical Argumentation: Principles of Theory and Practice, Sage. (In English)